

To remain conform to the notation used in previous papers dealing with the even-odd rule, compounds are noted in capitals: NH3 is for neutral ammonia, NH4(+) is an ammonia cation and NH2(−) an ammonia anion. This evidently removes solid structures from our study. far from extreme pressure and temperature. Ĭompounds used to illustrate the use of the table are known to exist under standard conditions in liquid or gaseous phase, i.e. This list is composed of compounds with elements of the main group. We end with a list of neutral and charged compounds compatible with the featured table. The difference between organic, semi-organic and inorganic elements is then detailed, linked to the number of electrons pairs in their shells. It describes features common to atoms within each cell as well as to neighboring cells. The specific periodic table for chemistry presents elements very similarly to the classical periodic table, with elements in rows and columns, but it additionally includes electronic structures of atoms when bearing charges.įirst, we briefly recall the rules used and presents the two first rows of the specific periodic table for chemistry.
Periodic table charges how to#
The even-odd rule gives the number of covalent bonds an element can have and the isoelectronicity rule allows to know where and how to add a charge when an element of a compound is needed. This specific table is based on the even-odd and the isoelectronicity rules recently proposed.

In this table, elements are classified by their number of electrons and their electronic structure in compounds, including when bearing charges. The present article is an attempt at addressing this limitation with a specific periodic table for chemistry. Understanding bonds and charges positions could be very useful in chemistry, mainly when studying compounds structures or predicting chemical reactions. Many variations of the periodic table exist, each trying to complete it for a specific purpose, but none gives indications of chemical bonds or of the location of electronic charges. This periodic table is today a reference even in chemistry.
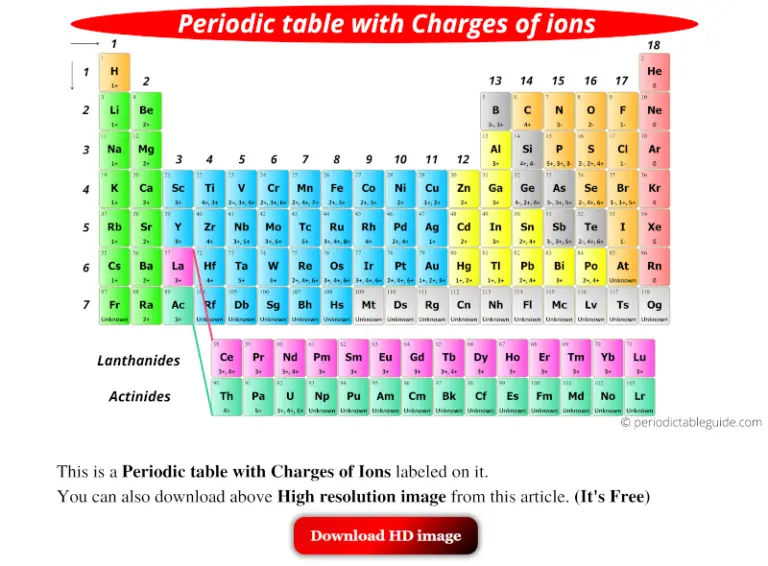
This periodic table classifies isotopes having the same positive charge, at the same place. The first parameter, the atomic weight, has been changed by Van den Broek who proposed to classify elements by their number of positive charges in the nucleus. The results evidence a connectionbetween electron solvation and reorientations of ice surface molecules.When Mendeleyev elaborated his periodic table in the 1860’s, he classified elements by their atomic weight and by columns containing elements with the same physical or valence properties. via STMor 2PPE experiments, and contribute significantly to their explanation.Apart from that nascent solvated electrons at the ice surface are offundamental interest, since they can induce reactions of adsorbates in awide range of energy and time scales. The theoreticalresults are entirely consistent with the observations, made e.g. Insight into direct neutralphotodissociation is given by subsequent BSE calculations. A characteristic scenario for the microscopic mechanisms and the relevantelectronic structures is found employing GW and underlying plane waveperiodic supercell DFT calculations. This is the first systematic ab-initio study providing a comprehensivepicture of activation and course of these intermediate chemical reactionsvia analysing prototypical adsorbed molecules (phenyl halogenides) and icesurface structures.

Beforehand photoexcited low-energyelectrons must attach dissociatively (DEA) to the CFCs on catalytically active icy grains in the terrestrial atmosphere. Nowadays industrially produced chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) substantiallymodify the global climate, since their emission leads to environmentallyhazardous ozone depleting reactions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
